Question 1
Show that \(\frac{1}{\tan \theta+\cot \theta}=\sin \theta \cos \theta\). [3]
Question 2
Find the coordinates of the points where the line \(2 y=x-1\) meets the curve \(x^{2}+y^{2}=29\). [5]
\(y=\frac{x-1}{2}\)
Substitute into \(x^{2}+y^{2}=29\)
\(x^{2}+\left(\frac{x-1}{2}\right)^{2}=29\)
\(\frac{4 x^{2}+(x-1)^{2}}{4}=29\)
\(4 x^{2}+x^{2}-2 x+1=116\)
\(5 x^{2}-2 x-115=0\)
\((5 x+23)(x-5)=0\)
\(x=\frac{-23}{5}, x=5\)
Substitute into \(y=\frac{x-1}{2}\)
\(\begin{aligned} x &=-\frac{33}{5} \\ y &=\frac{\left(-\frac{23}{5}\right)-1}{2} \\ &=-\frac{14}{5} \\ x &=5 \\ y &=\frac{5-1}{2} \\ &=2 \end{aligned}\)
The coordinate of the point are
\(\left(-\frac{23}{5},-\frac{14}{5}\right)\) and (5,2)
Question 3
(i) Express \(\log _{x} 2\) in terms of a logarithm to base 2. [1]
\(=\frac{\log _{2} 2}{\log _{2} x}\)
\(=\frac{1}{\log _{2} x}\)
(ii) Using the result of part (i), and the substitution \(u=\log _{2} x\), find the values of \(x\) which satisfy the equation \(\log _{2} x=3-2 \log _{x} 2\) [4]
\(\log _{2} x=3-2\left(\frac{1}{\log _{2} x}\right)\)
Substitute \(u=\log _{2} x\)
\(u=3-\frac{2}{u}\)
\(u-3=-\frac{2}{u}\)
\(u^{2}-3 u=-2\)
\(u^{2}-3 x+2=0\)
\((u-1)(u-2)=0\)
\(u=1, u=2\)
\(\begin{aligned} \log _{2} x_{1} &=1 \\ x_{1} &=2 \end{aligned}\)
\(\log _{2} x_{2}=2\)
\(x_{2}=4\)
Question 4
A curve has equation \(y=\left(3 x^{2}+15\right)^{\frac{2}{3}}\). Find the equation of the normal to the curve at the point where \(x=2\). [6]
\(y=\left(3(2)^{2}+15\right)^{\frac{2}{3}}\)
\(y=9\)
\(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{2}{3}\left(3 x^{2}+15\right)^{-\frac{1}{3}}(6 x)\)
\(\frac{d y}{d x}=4 x\left(3 x^{2}+15\right)^{-\frac{1}{3}}\)
\(\begin{aligned} & \text { When } x=2, \\ \frac{d y}{d x} &=4(2)\left(3(2)^{2}+(15)\right)^{-\frac{1}{3}}.\\ &=\frac{8}{\sqrt[3]{(12+(15)}} \\ &=\frac{8}{\sqrt[3]{27}} \\ &=\frac{8}{3} \end{aligned}\)
Gradient of the normal
\(m=-\frac{3}{8}\)
Equation of the normal
\(\begin{aligned} y-9 &=-\frac{3}{8}(x-2) \\ y-9 &=-\frac{3}{8} x+\frac{3}{4} \\ y &=\frac{39}{4}-\frac{3}{8} x \end{aligned}\)
Question 5
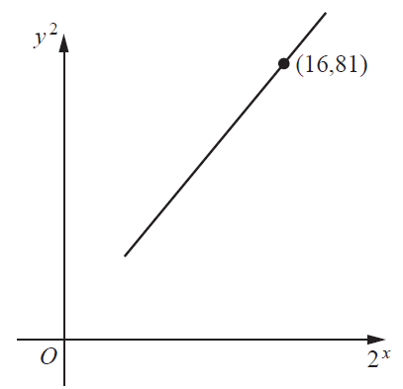
Variables \(x\) and \(y\) are such that, when \(y^{2}\) is plotted against \(2^{x}\), a straight line graph is obtained. This line has a gradient of 5 and passes through the point (16,81) .
(i) Express \(y^{2}\) in terms of \(2^{x}\). [6]
\( At (16,81) \)
\(81=5(16)+c \)
\(c=1\)
\(Y=y^{2}\)
\(X=2^{x}\)
\(m=5\)
\(c=1\)
Therefore
\(y^{2}=5\left(2^{2}\right)+1\)
(ii) Find the value of x when y = 6. [3]
\((6)^{2}=5\left(2^{x}\right)+1\)
\(5\left(2^{x}\right)=36-1\)
\(2^{x}=\frac{35}{5}=7\)
\(\lg 2^{x}=\lg 7\)
\(x=\frac{\lg 7}{\lg 2}=2.81\)
Question 6
(i) Given that \((3+x)^{5}+(3-x)^{5}=A+B x^{2}+C x^{4},\) find the value of \(A,\) of \(B\) and of \(C\). [4]
(ii) Hence, using the substitution \(y=x^{2},\) solve, for \(x,\) the equation \((3+x)^{5}+(3-x)^{5}=1086\). [4]
Question 7
(i) Show that \(\frac{(4-\sqrt{x})^{2}}{\sqrt{x}}\) can be written in the form \(p x^{-\frac{1}{2}}+q+r x^{\frac{1}{2}},\) where \(p, q\) and \(r\) are integers to be found. [3]
(ii) A curve is such that \(\frac{ d y}{ d x}=\frac{(4-\sqrt{x})^{2}}{\sqrt{x}}\) for \(x>0\). Given that the curve passes through the point (9,30) , find the equation of the curve. [5]
Question 8
The line \(C D\) is the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the point \(A(-1,-5)\) and the point \(B(5,3)\)
(i) Find the equation of the line \(C D\). [4]
\(\begin{array}{l}
m_{A B}=\frac{3+5}{5+1} \\
m_{A B}=\frac{4}{3}
\end{array}\)
\(\begin{aligned}
m_{A B} \times & m_{C D}=-1 \\
& m_{C D}=-\frac{3}{4}
\end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned} y+1 &=-\frac{3}{4}(x-2) \\ y &=-\frac{3}{4} x+\frac{1}{2} \end{aligned}\)
(ii) Given that \(M\) is the midpoint of \(A B\), that \(2 C M=M D\), and that the \(x\) -coordinate of \(C\) is -2 , find the coordinates of \(D .\) [3]
Equation of line \(C D\)
\(y=-\frac{3}{4} x+\frac{1}{2}\)
\(A+C\left(-2, y_{c}\right)\)
\(y_{c}=-\frac{3}{4}(-2)+\frac{1}{2}=2\)
\(\left(\frac{(1) x_{d}+2(-2)}{1+2}, \frac{(1) y_{d}+2(2)}{1+2}\right)=(2,-1)\)
\(\frac{x_{d}-4}{3}=2\)
\(x_{d}=10\)
\(\frac{y_{d} +2(2)}{3}=-1\)
\(y_{d}=-7\)
(iii) Find the area of the triangle \(C A D\). [2]
\(A=\frac{1}{2}|10+7+20+2+50-14|\)
\(A=\frac{1}{2}|75|\)
\(A=37.5\) unit \(^{2}\)
Question 9
(i) Given that \(y=x \sin 4 x,\) find \(\frac{ d y}{ d x}\). [3]
(ii) Hence find \(\int x \cos 4 x d x\) and evaluate \(\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{8}} x \cos 4 x d x\). [6]
\(\int(4 x \cos 4 x+\sin 4 x) d x=x \sin 4 x\)
\(\int 4 x \cos 4 x+\int \sin 4 x d x=x \sin 4 x\)
\(4 \int x \cos 4 x=x \sin 4 x-\int \sin 4 x d x\)
\(\int x \cos 4 x=\frac{1}{4} x \sin 4 x-\frac{1}{4}\left[-\frac{\cos 4 x}{4}\right]+c\)
\(=\frac{1}{4} x \sin 4 x+\frac{1}{16} \cos 4 x+c\)
\(\begin{aligned} & \int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{8}} x \cos 4 x d x \\=&\left[\frac{1}{4} x \sin 4 x+\frac{1}{16} \cos 4 x\right]_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{8}} \\=&\left[\frac{1}{4}\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right) \sin 4\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right)+\frac{1}{16} \cos 4\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\right]-\left[0+\frac{1}{16} \cos 0\right] \\=&\left[\frac{\pi}{32}(1)+0\right]-\frac{1}{16} \\=& \frac{\pi}{32}-\frac{1}{16} \end{aligned}\)
Question 10
(i) Solve \(2 \sec ^{2} x=5 \tan x+5,\) for \(0^{\circ}<x<360^{\circ}\). [5]
\(2\left(\tan ^{2} x+1\right)=5 \tan x+5\)
\(2 \tan ^{2} x+2=5 \tan x+5\)
\(2 \tan ^{2} x-5 \tan x-3=0\)
\(\tan x=y\)
\(2 y^{2}-5 y-3=0\)
\((2 y+1)(y-3)=0\)
\(y=-\frac{1}{2}, y=3\)
\(\begin{aligned} \tan & x=-\frac{1}{2} \\ x &=180^{\circ}-26.57^{\circ} \\ &=153.43^{\circ} \end{aligned}\)
or
\(\begin{aligned} x &=360^{\circ}-26 \cdot 57^{\circ} \\ &=333.43^{\circ} \end{aligned}\)
\(\begin{aligned} \tan x &=3 \\ x &=71.57^{\circ} \end{aligned}\)
or
\(\begin{aligned} x &=180^{\circ}+71.57^{\circ} \\ &=251.57^{\circ} \end{aligned}\)
(ii) Solve \(\sqrt{2} \sin \left(\frac{y}{2}+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=1,\) for \(0<y<4 \pi\) radians. [5]
\(0<\frac{y}{2}<2 \pi\)
\(\frac{\pi}{3}<\frac{y}{2}+\frac{\pi}{3}<2 \frac{1}{3} \pi\)
\(\sqrt{2} \sin \left(\frac{y}{2}+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=1\)
\(\sin \left(\frac{y}{2}+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\frac{y}{2}+\frac{\pi}{3}=\pi-\frac{\pi}{4}\)
\(\frac{y}{2}=\frac{3 \pi}{4}-\frac{\pi}{3}\)
\(\frac{y}{2}=\frac{5 \pi}{12}\)
\(y=\frac{5 \pi}{6}\)
or
\(\frac{y}{2}+\frac{\pi}{3}=2 \pi+\frac{\pi}{4}\)
\(\frac{y}{2}=\frac{9 \pi}{4}-\frac{\pi}{3}\)
\(y=\frac{23 \pi}{6}\)
Question 11
Answer only one of the following two alternatives.
EITHER
A curve has equation \(y= e ^{-x}(A \cos 2 x+B \sin 2 x)\). At the point (0,4) on the curve, the gradient of the tangent is 6
(i) Find the value of \(A\). [1]
(ii) Show that \(B=5\). [5]
(iii) Find the value of \(x\), where \(0<x<\frac{\pi}{2}\) radians, for which \(y\) has a stationary value. [5]
OR
A curve has equation \(y=\frac{\ln \left(x^{2}-1\right)}{x^{2}-1},\) for \(x>1\).
(i) Show that \(\frac{ d y}{ d x}=\frac{k x\left(1-\ln \left(x^{2}-1\right)\right)}{\left(x^{2}-1\right)^{2}},\) where \(k\) is a constant to be found. [4]
(ii) Hence find the approximate change in \(y\) when \(x\) increases from \(\sqrt{5}\) to \(\sqrt{5}+p\), where \(p\) is small. [2]
(iii) Find, in terms of e, the coordinates of the stationary point on the curve. [5]
