0 of 7 Questions completed Questions: You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading… You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You must first complete the following:
0 of 7 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
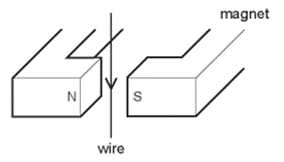
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0) A wire passes between the poles of a horseshoe magnet. There is a current in the wire in the direction shown, and this causes a force to act on the wire. (You may choose more than 1 answer.) The diagram shows a wire in the magnetic field between two poles of a magnet. A toy railway engine is driven around a track by a d.c. electric motor. The diagram shows a simple d.c. electric motor which is rotating. A metal rod \(P Q\) rests on two horizontal metal wires that are attached to a battery. The rod lies between the poles of a magnet. The diagram shows a thin copper wire in a magnetic field. The current in the wire is from right to left. This causes an upward force on the wire. The diagram shows a flat, rectangular coil placed between the poles of a magnet. There is a current in the coil that makes it turn in the direction shown in the diagram.
Quiz Summary
Information
Results
Results
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
Pos.
Name
Entered on
Points
Result
Table is loading
No data available
1. Question
1 point(s)
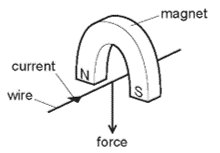
Three other arrangements, \(\mathrm{P}, \mathrm{Q}\) and \(\mathrm{R}\), of the wire and magnet are set up as shown below. Which arrangement or arrangements will cause a force in the same direction as the original arrangement?
2. Question
1 point(s)
The current in the wire repeatedly changes between a constant value in one direction and a constant value in the opposite direction. This is shown on the graph.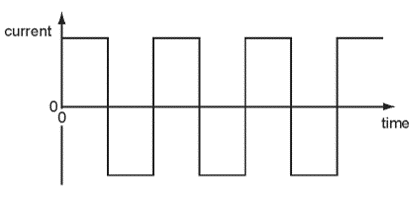 What is the effect on the wire?
What is the effect on the wire?
3. Question
1 point(s)
How can the speed of the motor be increased?
4. Question
1 point(s)
Which change will make the motor rotate more quickly?
5. Question
1 point(s)
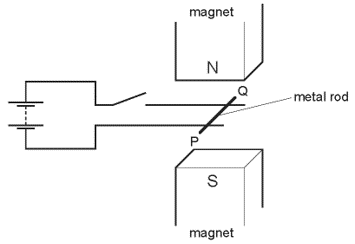
When the switch is closed, the rod moves to the right.
What could be changed so that the rod moves to the left?
6. Question
1 point(s)
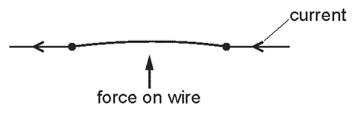
The direction of the current and the direction of the magnetic field are both reversed.
In which direction does the force act on the wire, after these changes are made?
7. Question
1 point(s)
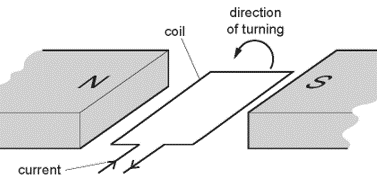
Which change would make the coil turn in the opposite direction?
0 of 7 Questions completed Questions: You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading… You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You must first complete the following:
0 of 7 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0) The diagram shows a coil of wire between the poles of a magnet. The diagram shows a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. Which device uses a split-ring commutator? A simple d.c. electric motor is fitted with a coil that rotates in a magnetic field. A commutator connects the power supply to the coil. The diagram shows a shaded area where the direction of a magnetic field is into the page. A current-carrying coil in a magnetic field experiences a turning effect. A current-carrying wire \(X Y\) lies in the magnetic field between the two poles of a \(U\)-shaped electromagnet. A force acts on the wire \(X Y\) because of the magnetic field. How many of these actions cause the direction of the force on the wire \(X Y\) to be reversed?
Quiz Summary
Information
Results
Results
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
Pos.
Name
Entered on
Points
Result
Table is loading
No data available
1. Question
1 point(s)
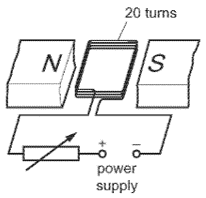
The coil consists of 20 turns of insulated wire.
The coil is connected to a variable resistor and a power supply.
How can the turning effect on the coil be increased?
2. Question
1 point(s)
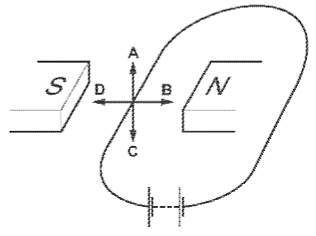
Which arrow shows the direction of the force acting on the conductor?
3. Question
1 point(s)
4. Question
1 point(s)
What is the purpose of the commutator?
5. Question
1 point(s)
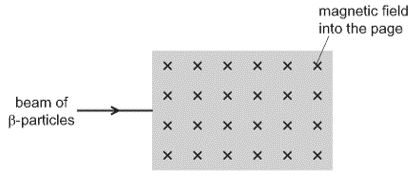 A beam of \(\beta\)-particles enters the field as shown.
A beam of \(\beta\)-particles enters the field as shown.
In which direction is the beam of \(\beta\)-particles deflected as they enter the magnetic field?
6. Question
1 point(s)
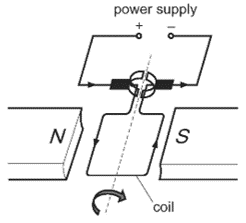
How can the turning effect be increased?
7. Question
1 point(s)
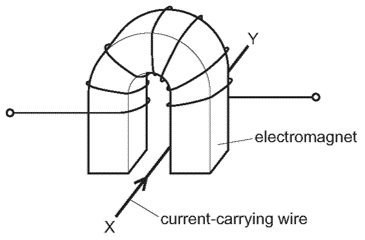
Each of the following actions is carried out separately.
