0 of 9 Questions completed Questions: You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading… You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You must first complete the following:
0 of 9 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0) A compound has the formula \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2\). \[ Which product is obtained when bromine reacts with propene, \(\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2\) ? Alkanes undergo substitution reactions with chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light. Increasing the number of atoms in one molecule of a hydrocarbon increases the amount of energy released when it burns. What is the correct order? During the process of cracking hydrocarbons, an ………. 1 ……….. is converted into an ……….. 2 ……….. . Which words complete gaps \(1,2,3\) and \(4\)? \[ A hydrocarbon A is cracked to make B and hydrogen. \[ The equation shows an industrial process. What is the name of compound X? X, Y and Z are three hydrocarbons. 1 They are all alkenes. The diagram shows a flow diagram. \[
Quiz Summary
Information
Results
Results
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
Pos.
Name
Entered on
Points
Result
Table is loading
No data available
1. Question
1 point(s)
Which row in the table shows the type of compound and the colour change when aqueous bromine is added?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { type of compound } & \text { colour change } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { saturated } & \text { brown to colourless } \\
\text { B } & \text { saturated } & \text { colourless to brown } \\
\text { C } & \text { unsaturated } & \text { brown to colourless } \\
\text { D } & \text { unsaturated } & \text { colourless to brown } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
2. Question
1 point(s)
3. Question
1 point(s)
Which equation shows a reaction of this type?
4. Question
1 point(s)
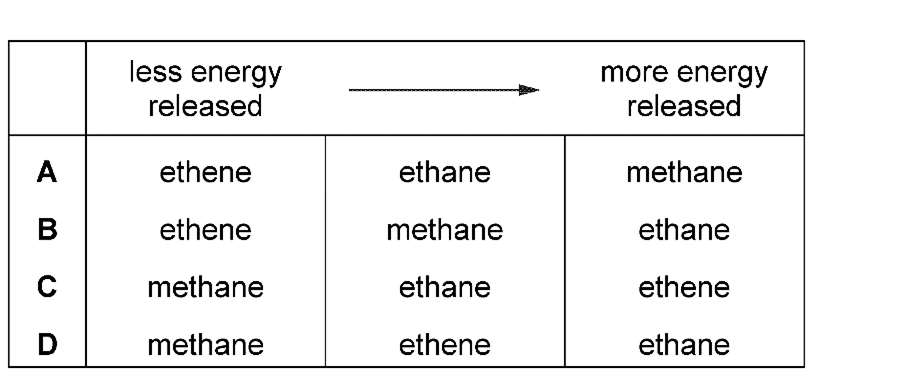
5. Question
1 point(s)
The presence of an ……….. 3 ………. can be shown by a visible reaction with ……….. 4 ………. .
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { alkane } & \text { alkene } & \text { alkene } & \text { bromine } \\
\text { B } & \text { alkane } & \text { alkene } & \text { alkene } & \text { steam } \\
\text { C } & \text { alkene } & \text { alkane } & \text { alkane } & \text { bromine } \\
\text { D } & \text { alkene } & \text { alkane } & \text { alkane } & \text { steam } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
6. Question
1 point(s)
Compound C is formed by the addition polymerisation of B.
To which homologous series do A, B and C belong?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { alkene } & \text { alkane } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { A } & \text { B and C } \\
\text { B } & \text { B } & \text { A and C } \\
\text { C } & \text { C } & \text { A and B } \\
\text { D } & – & \text { A and C } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
7. Question
1 point(s)

8. Question
1 point(s)
![]()
What do compounds X, Y and Z have in common?
2 They are all part of the same homologous series.
3 They all have the same boiling point.
9. Question
1 point(s)
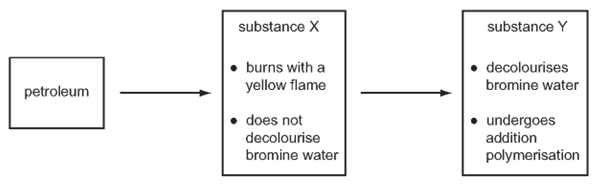
Which type of organic compounds are X and Y ?
\begin{array}{|l|c|l|}
\hline & \text { substance } X & \text { substance } Y \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { alcohol } & \text { alkane } \\
\text { B } & \text { alkane } & \text { alkene } \\
\text { C } & \text { alkene } & \text { alkane } \\
\text { D } & \text { alkane } & \text { alcohol } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
Alcohol
0 of 12 Questions completed Questions: You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading… You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You must first complete the following:
0 of 12 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0) What is not essential for the formation of ethanol by fermentation? Propanol is oxidised by acidified potassium manganate(VII) in a similar way to ethanol. Ethanol is made by fermentation of sugars and by the catalytic addition of steam to ethene. Ethanol can be formed by: 1 fermentation Which of these processes use a catalyst? \[ Which row describes an advantage and a disadvantage of making ethanol by fermentation? \[ The diagram shows a reaction sequence. \[ The structure of compound R is shown. Substance \(Z\) has the following characteristics. 1 It burns in an excess of oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. What is substance \(Z\) ? Ethanol is manufactured from petroleum by reacting ethene with steam. 1 Ethene is obtained from the cracking of alkanes. The diagram shows a reaction sequence. \[ The table shows the boiling points of four members of the homologous series of alcohols. Sugar can be fermented to produce ethanol. 1 Leave in a warm place. What is the correct order of these stages?
Quiz Summary
Information
Results
Results
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
Pos.
Name
Entered on
Points
Result
Table is loading
No data available
1. Question
1 point(s)
2. Question
1 point(s)
Which compound is produced by the oxidation of propanol with acidified potassium manganate(VII)?
3. Question
1 point(s)
What are two advantages of making ethanol by the catalytic addition of steam to ethene rather than by fermentation of sugars?
4. Question
1 point(s)
2 reaction between steam and ethene.
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & 1 & 2 \\
\hline \text { A } & \checkmark & \checkmark \\
\text { B } & \checkmark & x \\
\text { C } & x & \checkmark \\
\text { D } & x & x \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
5. Question
1 point(s)
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { advantage } & \text { disadvantage } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { uses a renewable resource } & \text { occurs at a slow rate } \\
\text { B } & \text { needs a high temperature } & \text { produces impure ethanol as a product } \\
\text { C } & \text { produces pure ethanol as a product } & \text { needs a high temperature } \\
\text { D } & \text { occurs at a slow rate } & \text { uses a non-renewable resource } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
6. Question
1 point(s)
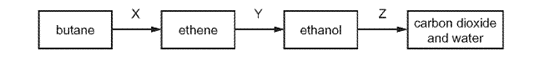
Which row names the processes X, Y and Z ?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \mathrm{X} & \mathrm{Y} & \mathrm{Z} \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { cracking } & \text { fermentation } & \text { respiration } \\
\text { B } & \text { cracking } & \text { hydration } & \text { combustion } \\
\text { C } & \text { distillation } & \text { fermentation } & \text { respiration } \\
\text { D } & \text { distillation } & \text { hydration } & \text { combustion } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
7. Question
1 point(s)
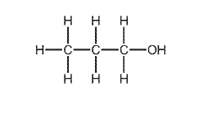
What is R?
8. Question
1 point(s)
2 It is oxidised by air to form a liquid smelling of vinegar.
3 It reacts with carboxylic acids to form esters.
9. Question
1 point(s)
Which statements about this process are correct?
2 The process is carried out in the presence of yeast.
3 The reaction is an addition reaction.
4 The rate of reaction is increased by a catalyst.
10. Question
1 point(s)
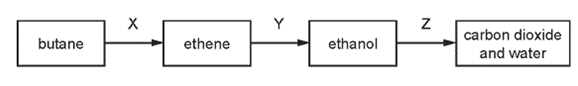
Which row names the processes X, Y and Z ?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \mathrm{X} & \mathrm{Y} & Z \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { cracking } & \text { fermentation } & \text { respiration } \\
\text { B } & \text { cracking } & \text { hydration } & \text { combustion } \\
\text { C } & \text { distillation } & \text { fermentation } & \text { respiration } \\
\text { D } & \text { distillation } & \text { hydration } & \text { combustion } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
11. Question
1 point(s)
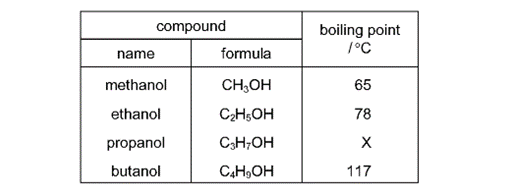
What is the value of X ?
12. Question
1 point(s)
Some of the stages in the process to produce and purify ethanol are listed.
2 Add yeast.
3 Fractionally distil the solution.
4 Dissolve the sugar in water.
5 Filter to remove the yeast.
6 Crush some sugar cane.
Corboxylic Acids
0 of 10 Questions completed Questions: You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading… You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You must first complete the following:
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0) Which statement about aqueous ethanoic acid is correct? Which statement about ethanoic acid is correct? Which statement describes the compound shown below? Molecule \(X\) is both an alkene and a carboxylic acid. \[ Which structure shows a carboxylic acid? Which esters have the molecular formula \(\mathrm{C}_5 \mathrm{H}_{10} \mathrm{O}_2\) ? 1 ethyl propanoate The structure of an ester is shown. \[ The structure of an alkene and the structure of an ester are shown. \[ The structure of ester W is shown. \[ The structure of an ester is shown. \[
Quiz Summary
Information
Results
Results
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
Pos.
Name
Entered on
Points
Result
Table is loading
No data available
1. Question
1 point(s)
2. Question
1 point(s)
3. Question
1 point(s)
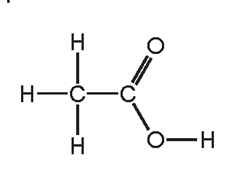
4. Question
1 point(s)
Which row describes \(X ?\)
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { saturated } & -\mathrm{COOH} \text { present } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { no } & \text { no } \\
\text { B } & \text { no } & \text { yes } \\
\text { C } & \text { yes } & \text { no } \\
\text { D } & \text { yes } & \text { yes } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
5. Question
1 point(s)
6. Question
1 point(s)
2 propyl ethanoate
3 butyl methanoate
4 methyl butanoate
7. Question
1 point(s)
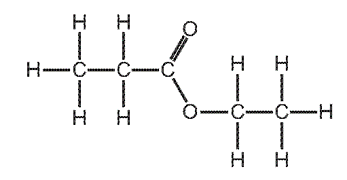
Which alcohol and carboxylic acid produce this ester?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { alcohol } & \text { carboxylic acid } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { ethanol } & \text { ethanoic acid } \\
\text { B } & \text { ethanol } & \text { propanoic acid } \\
\text { C } & \text { propanol } & \text { ethanoic acid } \\
\text { D } & \text { propanol } & \text { propanoic acid } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
8. Question
1 point(s)
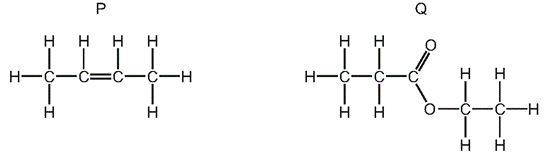
What are the names of P and Q?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{Q} \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { but-1-ene } & \text { ethyl propanoate } \\
\text { B } & \text { but-1-ene } & \text { propyl ethanoate } \\
\text { C } & \text { but-2-ene } & \text { ethyl propanoate } \\
\text { D } & \text { but-2-ene } & \text { propyl ethanoate } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
9. Question
1 point(s)
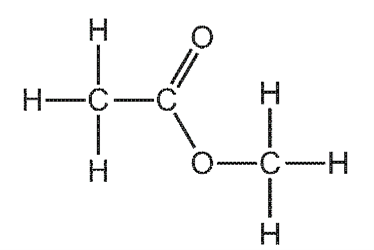
Which row gives the names of ester W and the carboxylic acid and alcohol from which it is made?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { name of ester W } & \text { carboxylic acid } & \text { alcohol } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { ethyl methanoate } & \text { ethanoic acid } & \text { methanol } \\
\text { B } & \text { ethyl methanoate } & \text { methanoic acid } & \text { ethanol } \\
\text { C } & \text { methyl ethanoate } & \text { ethanoic acid } & \text { methanol } \\
\text { D } & \text { methyl ethanoate } & \text { methanoic acid } & \text { ethanol } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
10. Question
1 point(s)
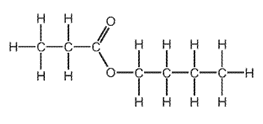
Which combination of carboxylic acid and alcohol produces this ester?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { carboxylic acid } & \text { alcohol } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { butanoic acid } & \text { ethanol } \\
\text { B } & \text { butanoic acid } & \text { propanol } \\
\text { C } & \text { ethanoic acid } & \text { butanol } \\
\text { D } & \text { propanoic acid } & \text { butanol } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
Polymers
0 of 8 Questions completed Questions: You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading… You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz. You must first complete the following:
0 of 8 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0) Which row describes the formation of a polymer? \[ Which equation represents the formation of poly(propene) from propene? The diagram shows the structure of a monomer and of the polymer made from it. \[ A section of a polymer is shown. The structure of a polymer is shown. A polymer linkage contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen atoms. \[ The equation shows the formation of a polymer called Kevlar. \[ The diagram shows part of the molecule of a polymer.
Quiz Summary
Information
Results
Results
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
Pos.
Name
Entered on
Points
Result
Table is loading
No data available
1. Question
1 point(s)
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { monomer } & \text { polymer } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { ethane } & \text { poly(ethane) } \\
\text { B } & \text { ethane } & \text { poly(ethene) } \\
\text { C } & \text { ethene } & \text { poly(ethane) } \\
\text { D } & \text { ethene } & \text { poly(ethene) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
2. Question
1 point(s)
3. Question
1 point(s)
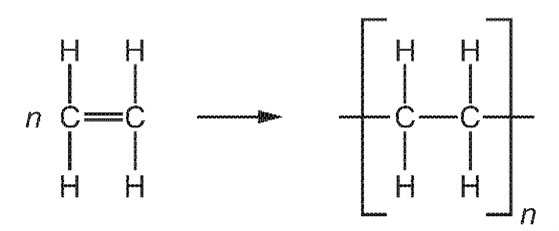
What are the monomer and polymer?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { monomer } & \text { polymer } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { ethane } & \text { poly(ethane) } \\
\text { B } & \text { ethane } & \text { poly(ethene) } \\
\text { C } & \text { ethene } & \text { poly(ethane) } \\
\text { D } & \text { ethene } & \text { poly(ethene) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
4. Question
1 point(s)
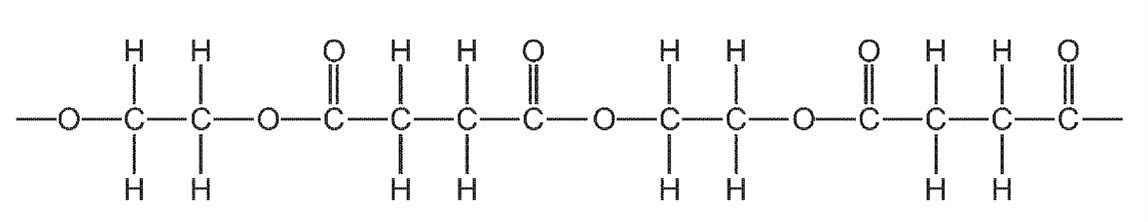
How many different types of monomer units formed this section of polymer?
5. Question
1 point(s)
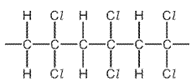
Which monomer is used to make this polymer?
6. Question
1 point(s)
Which row about the polymer is correct?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \begin{array}{c}
\text { type of } \\
\text { polymer }
\end{array} & \text { formed by } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { polyamide } & \text { addition polymerisation } \\
\text { B } & \text { polyamide } & \text { condensation polymerisation } \\
\text { C } & \text { polyester } & \text { addition polymerisation } \\
\text { D } & \text { polyester } & \text { condensation polymerisation } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
7. Question
1 point(s)
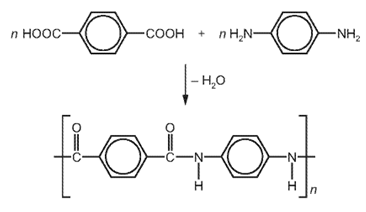
Which row describes Kevlar?
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { how the polymer is formed } & \text { type of polymer } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { addition polymerisation } & \text { polyamide } \\
\text { B } & \text { addition polymerisation } & \text { polyester } \\
\text { C } & \text { condensation polymerisation } & \text { polyamide } \\
\text { D } & \text { condensation polymerisation } & \text { polyester } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]
8. Question
1 point(s)
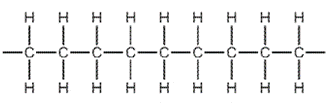
Which diagram shows the monomer from which this polymer could be manufactured?
